SUMMARY:
The role of workers:
Human potential has been considered as one of the most important asset for any company in the world. Sometimes it has been exploited and underpaid because the need of the companies of cost reductions. However, the labor force is taking more power although the technological advances are the new trend nowadays.
Workers have benefits that they did not have before: health and safety for them and their families, education, and other privileges than motivate them to do better things for the companies. This strategy has been implemented since the organizations realized that human resources are a key factor of success or default in the performance of outcomes for a company.
That is why today there are a lot of labor unions, trade unions and many other organizations giving even more participation to the employees because it means that they are more prepared for participate in the decision making processes.
In the recommended reading for this topic (UNDERSTANDING MANAGEMENT GERMAN-STYLE) we can see clearly how the European companies have involved their employees in decision making process and specially in German style, how those employees make part of a “consensus” and how the trade unions lead by workers might influence in management decisions: “When an agreement is reached, everyone works together to help the company move forward... in Germany, a whole chain is involved but the difference is that once the decision has been taken there, it will be rigorously implemented”
Migrant Workers:
Migrant workers could be defined as the people who voluntarily or involuntarily have moved from one specific place to another in order to work or look for a job.
Those people are having a strong importance nowadays because this situation are changing the policies applied by the countries due to the labor force supply and demand according the population and organizations are managing this situation due to the diversity of people that they hire and policies of requirements for those kind of people within the organizations.
How can we differentiate the types of migrant workers? They can be divided in two categories: 1) voluntary or involuntary and 2) skilled and non-skilled workers. In the first category we find the workers that want to leave their home countries because they believe they will have better opportunities abroad, these are the voluntary migrant workers. At the same time we may find others that had to leave their countries because of social or economic problems that forces that worker to leave, these are the involuntary migration workers.
In this chart we can see clearly the push factors that influence people and workers to go to another place and look for new opportunities. The worldwide statistics show that unemployment and poverty are the principal factors because people are motivated to look for a better job and they see those pull factors in countries that are more developed because the find more opportunities there.
Many worldwide institutions as the United Nations have been working in order to control and protect migrant workers because they are victims of exploitation and unfair situations due to the lack of the education that most of them present.
“Over the past decade and a half, however, migrant domestic workers in Hong Kong — mostly Filipinas and Indonesian women — have become highly active, organizing and participating in political protests. Hong Kong's migrant domestic workers protest in a place where they are guest workers and temporary migrants, denied the opportunity of becoming legal citizens or permanent residents”.
Expatriate assignments and Overseas Experience:
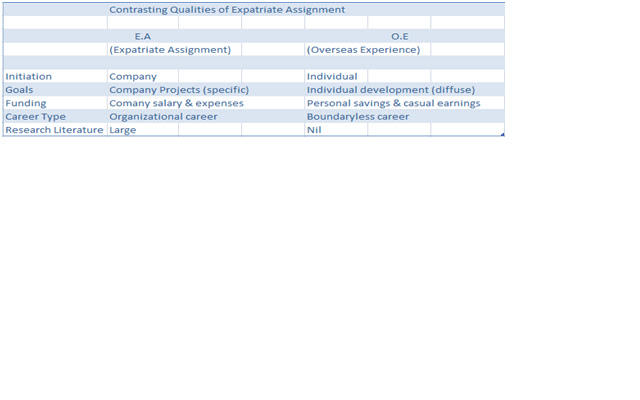
Nowadays, the tendency of international trade is to be more internationalized and the creation of new strategies in order to compete in local-regional markets and international markets. For this reason, companies are looking for people who have international experience, people who have visited and taken experiences from different places in order to construct or adapt those ideas in the host country or in the host company. We can see this experience in two types of international experiences that bring to the company new perspectives from their employees and then making them in strategies and products that help to the growth of employees and organizations at the same time. I will resort to the document written by Inkson et al (Inkson et al. 1999) titled "Expatriate assignments and overseas experience – contrasting models of international human resource development" in order to explain those two concepts and clarify the differences among them:
* In Expatriate Assignment (EA), the initiative for the international experience comes primarily from a company which operates internationally. In this process the company assigns a task for its employees in another country. This task might be since international recognition of markets or tendencies to international negotiations with customers in a foreign country.
* In Overseas Experience (OE), the initiative for the international experience comes from the individual. This process begins when a person decide to save money or get money from somewhere else with the main objective of go to another country and learn from this country (language, specific subject, or just experiences), then after a considerable time, this person returns to the home country and restart his career or decide to study another one.
Chart taken from: Inkson et al (Inkson et al. 1999):"Expatriate assignments and overseas experience – contrasting models of international human resource development"
Co-determination principles over the organization’s decision making process:
The co-determination principles is a organizational practice intruduced firstly by German companies, and it consists in the participation of employees in managerial practices and decisions. “the German model has a strong institutional framework but one which is flexible enough to adapt to change. Lane (1989) argues that the institutionalized system of worker representation in Germany results in a highly constrained industrial relations system which provides German labour with higher levels of power resources than employees in other countries.” (Avoidance strategies and the German system of co-determination, by Tony Royle).
This practice has had a strong impacts in many other countries as a model of “consensus” or learnig organizations where the decision making process is not centrized but it includes all the possible perspectives from employees who are sometimes customers and bring good ideas for the organization development.
From the managerial perspective we could find some advantages and disadvantages for this kind of flexible structures:
- To reduce management-labour conflict by means of improving and systematizing communication channels
- Small but important effect in the final performance of the company
- The opportunity to correct the existent failures in the company that the management board could not perceive before
- However, if the company does not apply restrictions an laws for this practice, it might become as a flexible and weak organization where the decision making process become more complex because the number of actors that have to reach an agreement and a point of accordance
Employee’s perspective:
- Employees could have more loyalty for the company if they feel that they are making good things for the company that they work to.
- In systems with co-determination the employees are given seats in a board of directors in one-tier management systems or seats in a supervisory board
“In general, the principle of ‘codetermination’ (loosely translated in French by ‘joint management’ but not in the literal sense) implies that one appoints people who are competent and capable of having discussions with the employers in a skilled supervisory board. Yet, the trade unions have their own academics” (Taken from: UNDERSTANDING MANAGEMENT GERMAN-STYLE)
Recommended readings:
- Piette, Jean-Jacques. 2004. “Understanding Management German style”. Les Amis de L’ecole de Paris.
- Inkson et al (Inkson et al. 1999): "Expatriate assignments and overseas experience – contrasting models of international human resource development"
- UNDERSTANDING MANAGEMENT GERMAN-STYLE

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario